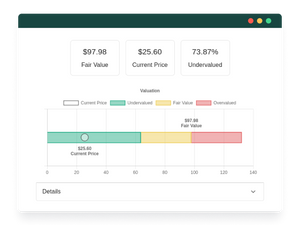
In value investing, the goal is to buy stocks that are undervalued, meaning that their intrinsic value is higher than their market price. This is usually referred as buying at a discount.
For example, imagine a company that is currently trading at $50 per share, but has a strong business model, a solid management team, and a growing market. A value investor might believe that the intrinsic value of the company is actually $60 per share, meaning it is undervalued. In this case, the value investor would want to buy shares of the company because they believe that in the future, the market will recognize the company's true value and the stock price will go up.
Intrinsic value is important in value investing because it helps investors identify opportunities to buy assets at a discount. By understanding the true value of a company or an asset, investors can make more informed decisions about when to buy and sell.
Intrinsic value is an estimate and it can be difficult to calculate. Different investors may have different opinions about the intrinsic value of a given asset or company, and this can lead to differences of opinion about whether an asset is truly undervalued.